Basics: What is a sanctions list and how is it checked?
A sanctions list is an official list of countries, individuals, organisations and, depending on the definition, goods that are subject to sanctions.
Such sanctions take the form of various restrictive or repressive measures. For example, they may restrict or prohibit passenger travel, financial transactions or international business relations. When business transactions with individuals or companies are subject to legal restrictions as part of sanctions, this is also referred to as an embargo. Specifically, sanctions can mean the restriction of economic resources such as raw materials or real estate, or the freezing of assets such as bank accounts.
The aim of these restrictions or reprisals is to combat:
- human rights violations, acts of war, terrorism
- the proliferation of dangerous weapons
- financial crime such as money laundering
- unfair competition
- cybercrime
- other unethical and illegal activities
Legal security for your company - with SANSCREEN
With SANSCREEN, you can play it safe. Check your business contacts manually or automatically against daily sanctions lists. With detailed and audit-proof logs, you can provide complete proof of your compliance measures if required.
Relevance: Who has to carry out sanctions checks?
All companies operating economically in the EU or based in the EU must ensure that none of their business partners are listed on the European Common Foreign & Security Policy (CFSP) list – this is stipulated by the relevant EU regulations and the Foreign Trade Act (AWG). This results in an indirect obligation to carry out checks. Organisations in the financial sector and foreign trade – such as banks or companies involved in exports and supply chains – are also explicitly required to check sanction lists.
Conclusion: Not only exporting companies, but also companies that only do business in Germany should check all business partners, suppliers, customers and employees against the various sanction lists.
Sales
No weapons, goods, money or information may flow to people, groups, organizations or companies that are on a sanctions list. Therefore, simply making an offer can result in you violating anti-terror regulations. The offer can theoretically be used to raise funds from e.g. B. to preserve banks and thus promote terrorism.
It is therefore advisable to check new business partners before exchanging information.
Purchasing
Purchasing must ensure that services or goods are only purchased from suppliers who are not on a sanctions list.
HR/Recruiting
In human resources, screening employees is controversial. Because it violates data protection guidelines. However, it must be ensured that no employee who is listed on a sanctions list is allowed to receive money.
Especially when new employees are being sought, it is advisable to check them early in the application phase.
Reasons: Why must the sanctions list check be carried out?
Regardless of whether your company is involved in import or export, management is obliged to carry out business partner screening. It must ensure that customers, suppliers, organisations and individuals are not listed on a sanctions list or an anti-terrorism list. If this is the case, the contact in question may not receive any goods, services or financial contributions. There are various reasons for this:
- Potential damage to reputation: Contacts with sanctioned individuals, organisations or countries may be viewed critically by the public and lead to a negative corporate image.
- Legal compliance: Sanctions list checks are necessary to comply with legal requirements. Failure to comply can result in fines and imprisonment. The persons affected are primarily managing directors and, in some cases, those responsible for exports.
- Economic risks: Without regular checks against sanctions lists, companies take on high risks. For example, a company in Europe or the UK may come into conflict with US sanctions law, even if local legislation would not be an issue.
Background: What are the legal bases for…
…sanctions list screening of business partners and customers?
The legal bases for sanctions list screening vary depending on the country and legal system:
- In the European Union, for example, sanctions list checks are regulated by the respective EU regulations and decisions. These regulations and decisions specify which persons or organisations are to be placed on the sanctions lists and which measures must be taken to comply with the sanctions.
- In Germany, Section 34 of the Foreign Trade and Payments Act must also be observed, and in Switzerland, the SECO embargo regulations.
… Sanctions list screening of employees?
The screening of employees against EU sanctions lists has been recognised as a legal basis by case law under Section 26(1) of the Federal Data Protection Act (BDSG). According to this provision, personal data may be processed for the purposes of the employment relationship, especially if this is necessary for the establishment, implementation or termination of the employment relationship. Further authorisation would then arise if the screening of employees is carried out on the basis of a law or a works agreement. Regular wage payments by the employer require that the employee is not listed on sanctions lists (especially those of the EU). Thus, the employer’s own employees may be checked accordingly. The same applies to AEO certification, because employees in security-relevant areas in particular must be checked against sanctions lists.
Free e-book on sanctions list screening
We have summarised everything you need to know about sanctions list screening in the EU in an e-book (only in german available).
The e-book covers the following topics:
-
- Why is sanctions list screening so important?
- What exactly is a sanctions list?
- Who has to check against sanctions lists?
- How often do checks have to be carried out?
- Which sanctions have to be checked against?
- …and much more
Which sanctions lists should be checked?
All currently valid sanctions lists must always be observed. These include the various EU sanctions lists, but also, for example, US sanctions lists. We provide a brief overview of existing lists in our article on sanctions lists. To cover all important sanctions lists during the check, we recommend using secure software for sanctions screening.
What data needs to be checked?
A thorough sanctions list check requires a careful comparison between sanctions lists and customer data, as well as data from business partners, suppliers and, where applicable, (future) employees. In addition to the name or the correct and complete company name, the following data can be useful for obtaining certainty after a similarity match:
- For individuals: surname and first name, date of birth, nationality
- For companies: legal form of the organisation, registration number, name of the managing director
How does a sanctions check work?
The typical process for a thorough sanctions check includes:
- Defining the individuals or companies to be checked and researching the relevant data
- Researching relevant sanctions lists
- Comparing the data records – manually or automatically using software
- Analysing possible matches to rule out potential errors
- In the case of genuine matches: Initiating measures (e.g. terminating business transactions and notifying the relevant authorities)
Automated or manual testing?
The manual check and the necessary documentation (customs, BAFA) of the processes result in a lot of effort. Thanks to automated queries in the background and connection to the ERP system, software for sanctions list screening can be an attractive solution. Then the address creation, address change or even just the address usage can be checked at any time. SANSCREEN is integrated into SAP ® ERP, SAP S/4HANA®, Dynamics NAV, Dynamics AX, Sage and APplus and many other systems available.
Automate the check with SANSCREEN.
What are false positives on sanctions lists?
If there is a similarity or even an exact match between names in your company database and a sanctions list, this can lead to false positives. In any case, a thorough investigation is necessary; the more data available for this, the better.
What to do if a contact is affected by sanctions?
- Involve your internal compliance officers.
- Document the result, including the date of the check, the sanctions list and the exact match. The relevant authorities may require a template under certain circumstances.
- Terminate all business relationships immediately. For example, do not pay out any funds and stop providing services.
- Report the sanctions list match to the relevant authorities, such as the Bundesbank or the BAFA.
Free online tools: How can I check for free?
FiSaLis – Ministry of Justice of North Rhine-Westphalia
In Germany, the Ministry of Justice of North Rhine-Westphalia offers a free online service to check addresses against EU sanctions lists.
The check refers solely to the EU Regulation 881/2002. However, according to the textual description, it can be assumed that the entire consolidated EU list will be used as the data basis for the check.
Under http://www.finanz-sanktionsliste.de You can search for possible matches with the selection of 3 levels 100, 80 and 60% match.

Source: finanz-sanktionsliste.de

Sanction map
The EU Sanction Map has been offering a good and appealing alternative since summer 2017.
The EU sanctions world map, which was implemented by the Estonian side, offers a very user-friendly sanctions list check with a clear presentation of the results. The application is available in English at https://www.sanctionsmap.eu/.
The graphical representation is clearly laid out Countries affected by sanctions as well as a list of all measures, goods, companies and people affected. The relevant legal act of the European Union is directly linked.
Sanktionslisten-online.de – only available in German
We offer complete documentation with our self-developed online tool for sanction list checking. Comprehensive checks on the 15 most important sanctions lists can be carried out via https://sanktionslisten-online.de/ (only available in German). The sanctions lists are updated daily and are obtained directly from the issuing authorities.
With the upload function it is possible to upload complete master data in a CSV file and have it checked. The results can be edited directly and enables long-term logging of the results. This means that released hits on the sanctions list can be transmitted to customs in a traceable manner if necessary.
You can register in just a few minutes.
OFAC (US sanctions lists only)
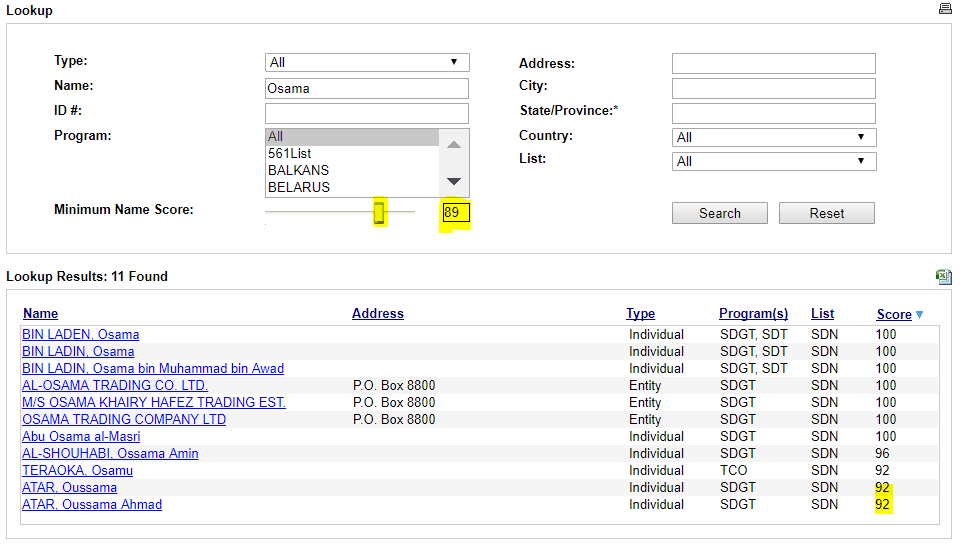
The Office of Foreign Asset Control (OFAC) offers a comprehensive review of US sanctions lists at https://sanctionssearch.ofac.treas. gov/. You can currently check for a match in 46 programs. What is interesting about this search is that the threshold of the fuzzy search can be adjusted using a slider. However, OFAC itself deliberately does not give any recommendation as to which setting should be used: “OFAC does not provide recommendations with regard to the appropriateness of any specific confidence rating”.
It is also pointed out that this search is only a tool and its use alone does not limit criminal or civil liability.
Source: sanctionssearch.ofac.treas.gov

Export.gov (US sanctions lists only)
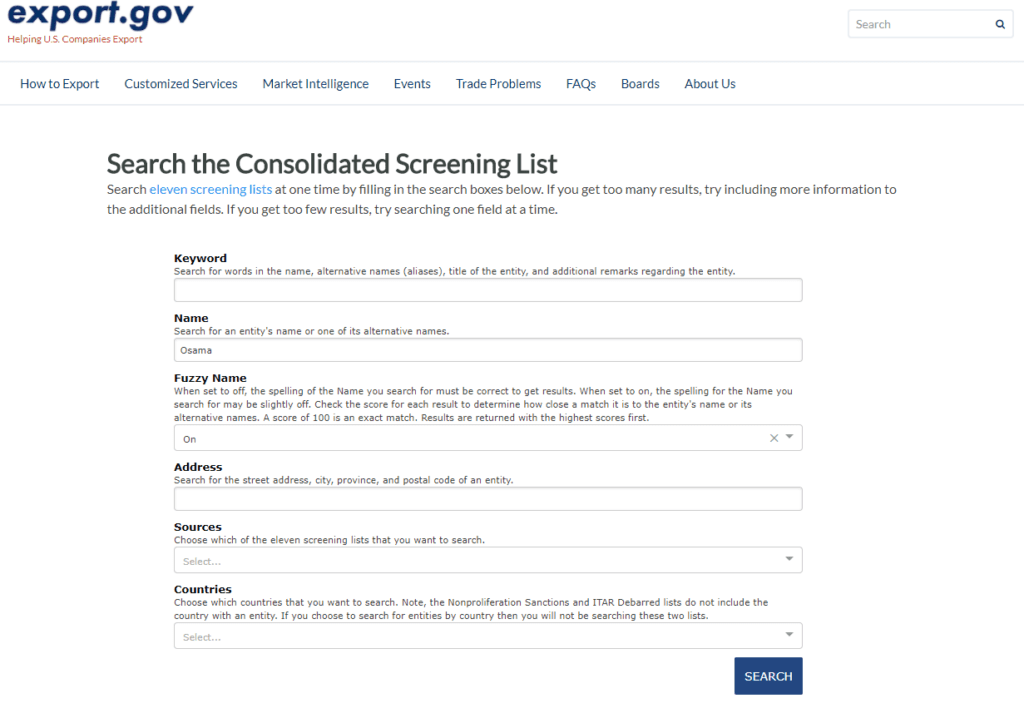
Alternatively, the International Trade Administration of the US Department of Commerce, together with 19 US government agencies, offers a
search tool on their website Export.gov, which is currently checking against 11 US lists, which can be found here https://www.trade.gov/consolidated-screening-list can be listed under Sources.
Source: https://www.trade.gov/export-solutions
There is also a switch for fuzzy search here. However, if you click on the view of the stored list entries, an unformatted desert of text appears. We therefore recommend using the OFAC list search and selecting this search only as an add-on for security purposes.




